Fibrocystic Breast Disease Specialist, often referred to as fibrocystic breast changes or fibrocystic breasts, is one of the most common benign (non-cancerous) conditions affecting women worldwide. Despite its prevalence, misconceptions and lack of awareness sometimes lead women to feel anxious or confused about their symptoms. The role of a fibrocystic breast disease specialist is pivotal in providing accurate diagnosis, reassurance, and appropriate management, ensuring women maintain their breast health and peace of mind.
What is Fibrocystic Breast Disease Specialist?
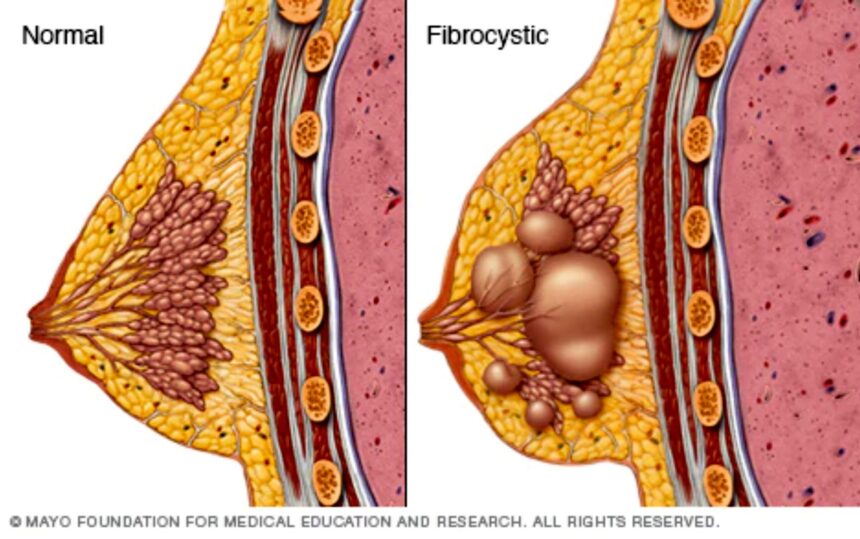
Fibrocystic Breast Disease Specialist is characterized by the presence of lumpy, dense, and often tender breast tissue. These changes are typically cyclical, fluctuating with the menstrual cycle, and can vary in severity from mild to quite uncomfortable. The condition involves the development of multiple benign cysts, fibrosis (thickening or scarring of tissue), and sometimes increased fibrous tissue within the breast.
It’s important to note that fibrocystic changes are extremely common, especially among women aged 20 to 50, and are considered a normal variation of breast tissue. Despite this, the symptoms can sometimes mimic those of more serious conditions, including breast cancer, which underscores the importance of expert evaluation.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
Women with Fibrocystic Breast Disease Specialist often report:
- Breast lumps: These are usually smooth, movable, and well-defined. They tend to fluctuate in size during the menstrual cycle.
- Breast pain or tenderness: Often described as dull or aching, pain may intensify before menstruation and subside afterward.
- Swelling or heaviness: Generalized discomfort or a feeling of fullness in the breasts.
- Nipple discharge: Occasionally, a clear or yellowish discharge may be present, though this is more common in other benign conditions.
The symptoms are usually bilateral (affecting both breasts) but can be more prominent on one side. The cyclical nature, with symptoms worsening before menstruation, is characteristic.
The Role of the Specialist in Fibrocystic Breast Disease
Given the commonality and benign nature of fibrocystic changes, women often seek consultation for reassurance or to determine if their symptoms warrant further investigation. The Fibrocystic Breast Disease Specialist, typically a breast surgeon, radiologist, or a gynecologist with expertise in breast health, plays a crucial role in:
- Accurate diagnosis
- Differential diagnosis to rule out other conditions
- Providing management strategies
- Offering reassurance and education
Diagnostic Approach
When a woman presents with breast lumps or discomfort, the specialist’s first priority is to distinguish benign fibrocystic changes from other potential issues, especially malignancies.
- Medical History and Physical Examination
The specialist begins by taking a detailed history, including the timing and nature of symptoms, menstrual cycle correlation, family history of breast cancer, and any prior breast issues. A thorough physical exam assesses the size, location, mobility, and consistency of lumps, plus skin changes or nipple abnormalities.
- Imaging Studies
- Mammography: Recommended, especially for women over 40 or when a lump persists beyond typical cyclical changes. Mammograms can differentiate cystic from solid lesions.
- Ultrasound: Particularly useful in younger women with dense breasts. Ultrasound can identify cysts (fluid-filled sacs) and solid masses, guiding further management.
- Fine-Needle Aspiration or Cyst Aspiration
If a cyst is identified, the specialist may perform a fine-needle aspiration to drain fluid. If the fluid is straw-colored or clear and the cyst resolves, it confirms a benign cyst. Sometimes, fluid analysis is done to rule out infection or blood.
- Biopsy
If a lump appears suspicious or does not resolve after aspiration, a core needle biopsy may be performed to exclude malignancy.
Management Strategies
Since Fibrocystic Breast Disease Specialist changes are benign, management aims to alleviate symptoms and provide reassurance. The specialist tailors treatment based on severity, symptom impact, and patient preferences.
- Lifestyle and Self-Care Measures
- Supportive Bra: Wearing a well-fitted, supportive bra reduces discomfort.
- Dietary Adjustments: Reducing caffeine intake may lessen breast pain in some women.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter analgesics like acetaminophen or NSAIDs can help manage tenderness.
- Warm or Cold Compresses: Applying heat or cold packs to the breasts can provide symptomatic relief.
- Medications
- Hormonal Therapy: In some cases, hormonal agents like oral contraceptives may be prescribed to regulate hormonal fluctuations that exacerbate symptoms.
- Vitamin Supplements: Some women find relief with vitamin E or evening primrose oil, though evidence varies.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular breast self-examinations and periodic clinical assessments are encouraged, especially if cysts or lumps are present. Follow-up imaging may be recommended to monitor changes over time.
- Addressing Anxiety and Providing Reassurance
Many women experience anxiety about breast lumps due to fear of cancer. The specialist’s role includes educating women on the benign nature of their condition, explaining diagnostic findings, and reassuring them about their breast health.
When to Seek Further Evaluation
While fibrocystic changes are benign, certain features warrant further investigation:
- Lumps that do not fluctuate with the menstrual cycle.
- Lumps that are hard, fixed, or irregular.
- Skin changes over the breast, nipple retraction, or discharge containing blood.
- Rapidly enlarging lumps.
- Persistence of symptoms beyond a few menstrual cycles.
In such cases, the specialist may recommend additional imaging, biopsy, or referral to a breast cancer specialist.
The Importance of Specialist Care
While general practitioners and gynecologists are equipped to evaluate breast complaints, a specialist with expertise in breast health offers nuanced assessment and management. They are familiar with subtle diagnostic cues and advanced imaging techniques, enabling precise differentiation between benign and suspicious lesions.
Furthermore, specialists play a vital role in patient education, dispelling myths, and reducing unnecessary anxiety and interventions. Their guidance ensures women receive appropriate care without over-treatment, thus maintaining breast health and psychological well-being.
Conclusion
Fibrocystic Breast Disease Specialist, although common and benign, can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life due to discomfort and anxiety. The fibrocystic breast disease specialist acts as a cornerstone in the comprehensive management of this condition, providing accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment, and reassurance.
Understanding the nature of fibrocystic changes helps women navigate their symptoms confidently. With appropriate care, most women experience relief from discomfort and can continue their daily activities without undue concern. Regular breast self-examinations, routine screenings, and consultations with a qualified specialist are key components of proactive breast health management.
In a healthcare landscape where breast health concerns are prevalent, the role of the fibrocystic breast disease specialist remains indispensable—ensuring that benign changes are distinguished from more serious conditions and that women receive compassionate, informed care tailored to their needs.