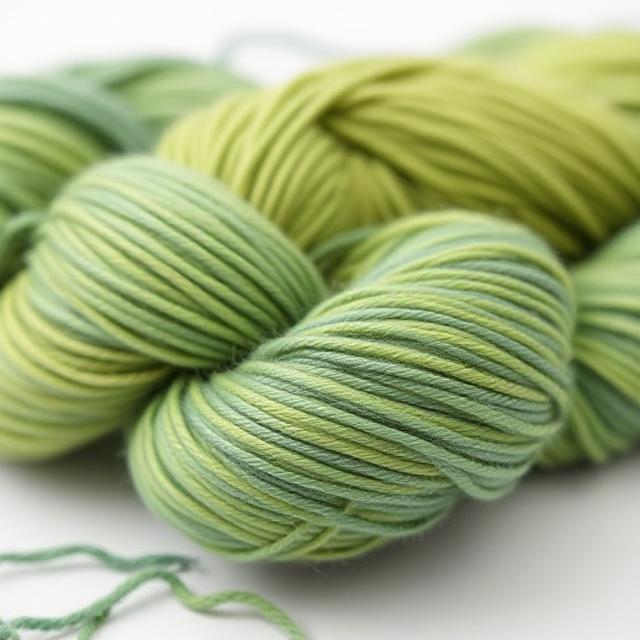
Introduction oto Dandoh Yarn
In the rich tapestry of Nigerian cultural heritage, textiles occupy a central role, serving as expressions of identity, social status, and artistic creativity. Among the myriad traditional fabrics woven and crafted across Nigeria, “Dandoh Yarn” stands out as a distinctive and culturally significant textile, embodying centuries of history, craftsmanship, and evolving innovation. This article explores the origins, cultural importance, technical aspects, and contemporary relevance of Dandoh Yarn, shedding light on its enduring legacy within Nigerian society.
Origins and Historical Context
Dandoh Yarn finds its roots in the indigenous weaving and dyeing traditions of Nigeria, particularly among the communities in the northern and central regions. While specific origins vary among different ethnic groups, the fabric is generally associated with communities that have a long-standing heritage of textile production, such as the Hausa, Yoruba, and neighboring groups.
Historically, the production of Dandoh Yarn was intertwined with communal activities, spiritual practices, and social ceremonies. The process of creating the yarn involved meticulous hand-spinning, dyeing, and weaving techniques passed down through generations. This craftsmanship was often a communal endeavor, fostering social bonds and cultural continuity.
The Significance of Dandoh Yarn in Nigerian Society
Dandoh Yarn is more than just a fabric; it is a symbol of cultural identity and social symbolism. Its use spans various aspects of life, including:
- Ceremonial Uses: Dandoh Yarn is prominently featured in traditional ceremonies such as weddings, festivals, and rites of passage. Its vibrant colors and intricate patterns serve as visual markers of cultural pride and heritage.
- Status and Identity: In some communities, the quality, color, and design of Dandoh-Yarn indicate social status, age, or community affiliation. For instance, certain patterns might be reserved for royals or elders, denoting respect and honor.
- Artistic Expression: The fabric serves as a canvas for artisans to showcase their creativity, employing unique motifs and dyeing techniques that reflect cultural stories, proverbs, and historical narratives.
Technical Aspects of Dandoh Yarn Production
The creation of Dandoh Yarn involves a complex series of traditional processes that highlight the skills and artistry of Nigerian artisans:
1. Spinning
The process begins with spinning natural fibers—most commonly cotton, silk, or locally sourced plant fibers—into yarn. Artisans use traditional spinning tools like spindles or hand-held spinning wheels, carefully controlling tension and twist to produce even, durable yarn.
2. Dyeing
Dyeing is a critical step that imparts the vibrant colors characteristic of Dandoh-Yarn. Traditionally, natural dyes derived from plants, roots, and minerals are used. For example, indigo for blue, madder root for red, and various local herbs for yellow and green hues. The dyeing process involves multiple stages of boiling, soaking, and sometimes mordanting (treating fibers with mordants to fix dyes), resulting in rich, long-lasting colors.
3. Weaving
Once the yarn is prepared, skilled weavers employ traditional loom techniques to produce the fabric. The weaving patterns can range from simple geometric motifs to complex, symbolic designs. The weaving process often involves trial and error, with artisans experimenting to develop new patterns and textures.
4. Embellishment
In some cases, Dandoh Yarn is further embellished through embroidery, beading, or additional dyeing techniques to enhance its aesthetic appeal and symbolic meaning.
Variants and Modern Adaptations
While traditional Dandoh Yarn remains deeply rooted in cultural practices, contemporary artisans and designers have innovated to adapt the fabric for modern tastes and markets. Some notable developments include:
- Hybrid Designs: Combining traditional motifs with modern fashion styles, Dandoh Yarn is now used in clothing, accessories, and home décor items.
- Commercial Production: Small-scale cooperatives and artisan groups have begun mass-producing Dandoh Yarn, making it accessible to a broader audience both within Nigeria and internationally.
- Fusion with Other Textiles: Artists blend Dandoh Yarn with other fabrics such as Ankara or Aso-oke to create fusion pieces that appeal to contemporary fashion trends.
Preservation Challenges and Cultural Revival
Despite its cultural significance, Dandoh Yarn faces several challenges:
- Loss of Traditional Skills: As younger generations migrate to urban areas and adopt modern lifestyles, the knowledge of traditional spinning, dyeing, and weaving techniques risks fading away.
- Economic Constraints: The labor-intensive nature of Dandoh Yarn production makes it less competitive against cheaper, machine-made textiles, threatening the livelihoods of artisans.
- Market Accessibility: Limited access to global markets and lack of branding hinder the wider dissemination of authentic Dandoh Yarn products.
In response, cultural organizations, NGOs, and government agencies have initiated efforts to preserve and promote Dandoh Yarn through:
- Cultural Festivals: Showcasing traditional textiles in festivals to raise awareness and pride.
- Training Programs: Providing skills transfer and apprenticeships to younger artisans.
- Market Development: Facilitating export opportunities and establishing boutiques that sell authentic Dandoh-Yarn products.
The Future of Dandoh Yarn
The future of Dandoh Yarn hinges on balancing tradition with innovation. As Nigerian designers incorporate Dandoh-Yarn into contemporary fashion and interior design, the fabric gains new relevance and visibility. Efforts to document and teach traditional techniques, coupled with branding that emphasizes authenticity and cultural heritage, can help sustain its production.
Furthermore, the global appreciation for ethically sourced and handcrafted goods presents opportunities for Dandoh-Yarn to find niche markets worldwide. By leveraging digital platforms, artisans can reach international consumers seeking unique, culturally rich textiles.
Conclusion
Dandoh Yarn embodies the rich cultural tapestry of Nigeria—an enduring symbol of artistry, community, and tradition. Its intricate craftsmanship, vibrant colors, and symbolic motifs reflect the diverse narratives of Nigerian societies. While challenges threaten its survival, ongoing efforts to preserve and innovate ensure that Dandoh-Yarn remains a vital part of Nigeria’s cultural heritage and continues to inspire future generations.
As Nigeria and the world increasingly embrace sustainable and artisanal products, Dandoh Yarn stands as a testament to the resilience of traditional crafts and the potential for cultural expression to thrive amidst modern change. Supporting artisans, promoting cultural education, and fostering innovative collaborations will be key to ensuring that Dandoh Yarn weaves its way into the future with strength and pride.