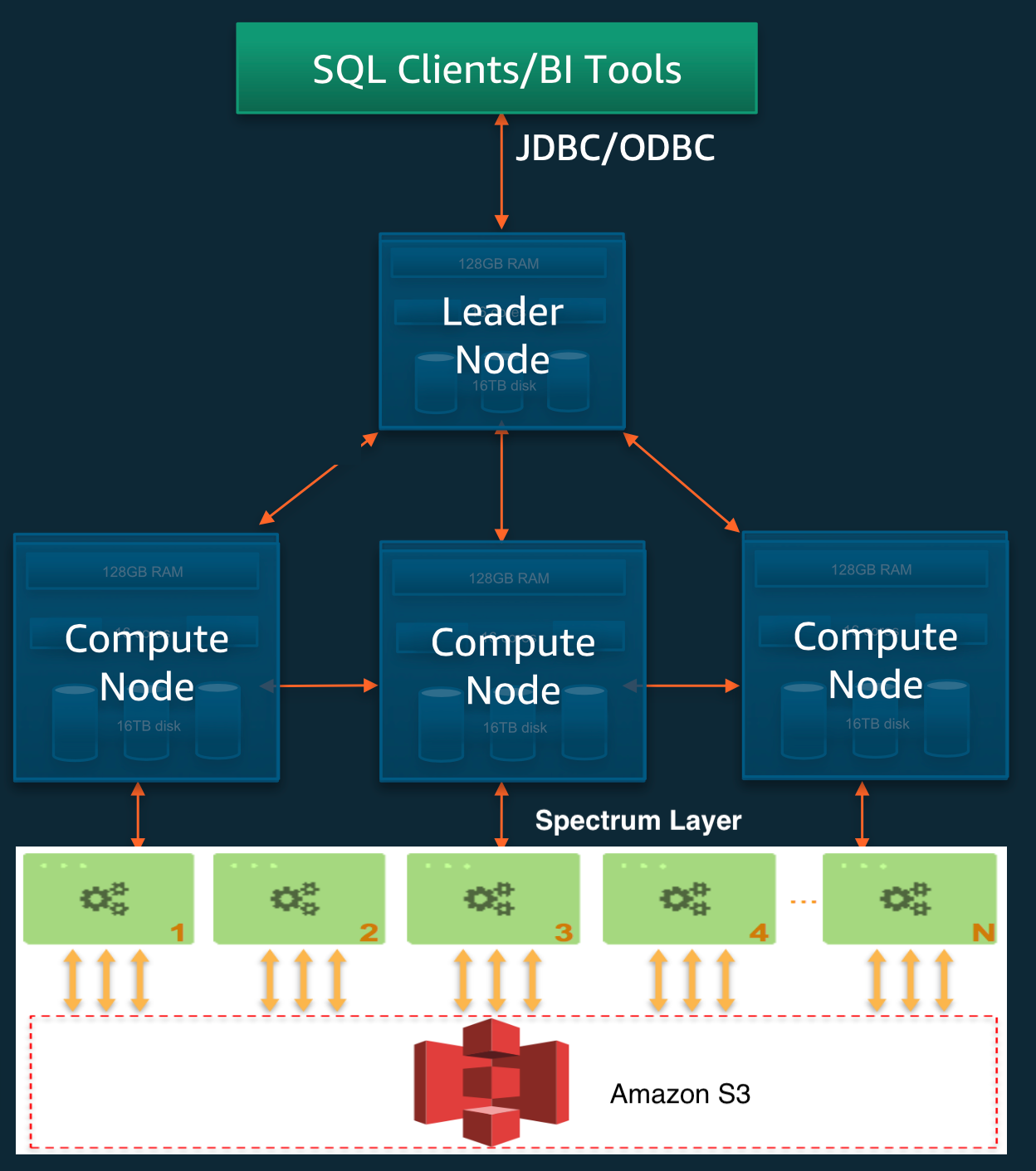
Amazon Redshift is a popular data warehousing solution that enables organizations to run complex queries and analyze large datasets efficiently. One of the common tasks in managing data warehouses is creating new tables that share the structure of existing ones. This process can be streamlined using the Redshift CREATE TABLE LIKE statement, which simplifies schema duplication without copying data. In this article, we’ll dive deep into how Redshift CREATE TABLE LIKE works in Redshift, its syntax, use cases, best practices, and alternative approaches.
What is the CREATE TABLE LIKE Statement?
In many relational database systems, including Redshift, the Redshift CREATE TABLE LIKE statement allows you to create a new table that inherits the structure of an existing table. This includes columns, data types, and potentially other attributes like constraints, distribution styles, and sort keys, depending on the syntax and options used.
Key points:
- Schema duplication: Quickly create a table with the same structure as an existing table.
- No data copying: Unlike
CREATE TABLE AS SELECT, it does not copy the data, only the schema. - Customization: Options can be specified to include or exclude certain aspects like constraints, defaults, or distribution keys.
Syntax of Redshift CREATE TABLE LIKE
The basic syntax in Redshift is as follows:
CREATE TABLE new_table LIKE existing_table [WITH [NO] DATA];new_table: The name of the table you want to create.existing_table: The table whose schema you want to clone.WITH DATA/NO DATA: Specifies whether to copy data along with the schema.NO DATAis default, meaning only the structure is copied.
Examples:
- Create an empty table with the same structure:
CREATE TABLE sales_backup LIKE sales NO DATA;- Create a table with the same structure and data:
CREATE TABLE sales_backup LIKE sales WITH DATA;However, note that in Redshift, the LIKE clause generally does not support WITH DATA or NO DATA. Instead, the default behavior is to copy only the schema, and for copying data, you typically use CREATE TABLE AS.
Important Considerations
- Default Behavior: In Redshift, Redshift CREATE
TABLE LIKEcopies only the table’s schema, including column definitions, distribution style, sort keys, and encoding if specified. - Constraints and Defaults: Redshift does not enforce constraints like primary keys or foreign keys, so these are not copied.
- Distribution and Sort Keys: These are copied, which is useful for maintaining query performance.
- Encoding: Column encoding is also copied, helping optimize storage.
Use Cases of Redshift CREATE TABLE LIKE
- Schema Replication: Quickly create a new table with the same structure as an existing one for testing, staging, or archiving purposes.
- Cloning for Data Transformation: Prepare a new table with the same structure before inserting transformed data.
- Backup or Versioning: Save the schema state before making significant changes.
- Partitioning or Segmentation: Create multiple similar tables for partitioning data by date, region, or other criteria.
Practical Examples
Example 1: Basic Schema Duplication
Suppose you have a table called orders:
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id INT,
order_date DATE,
customer_id INT,
total_amount DECIMAL(10,2)
)
DISTSTYLE KEY
DISTKEY (customer_id)
SORTKEY (order_date);To create a new empty table orders_backup with the same structure:
CREATE TABLE orders_backup LIKE orders;This command copies the column definitions, distribution style (DISTSTYLE KEY), distribution key (DISTKEY (customer_id)), and sort key (SORTKEY (order_date)).
Example 2: Cloning for Data Loading
While Redshift’s LIKE does not directly support copying data, you can combine schema duplication with data insertion:
-- Create the schema clone
CREATE TABLE new_table LIKE existing_table;
-- Insert data from existing table
INSERT INTO new_table SELECT * FROM existing_table WHERE condition;This approach allows you to create a schema clone and selectively copy data.
Limitations of Redshift CREATE TABLE LIKE in Redshift
While Redshift CREATE TABLE LIKE is powerful, it has some limitations:
- Constraints Not Copied: Redshift does not enforce constraints, so primary keys, foreign keys, or unique constraints are not transferred.
- Defaults and Triggers: Default values for columns are copied, but no triggers or stored procedures are involved.
- No Support for Indexes: Redshift does not support indexes beyond sort keys, so other index types are not relevant.
- Partial Schema Copy: Some attributes like comments, privileges, or table options are not copied.
Best Practices
- Explicitly Define Distribution and Sort Keys: When creating a clone, ensure that distribution style and sort keys are appropriate for the new table’s purpose.
- Use Redshift CREATE
TABLE LIKEfor Schema Duplication: For quick schema copying, especially when planning data loads or transformations. - Combine with
INSERT SELECT: To copy data into the new schema, combine schema creation with data insertion. - Maintain Naming Conventions: Use clear naming to distinguish between original and cloned tables to avoid confusion.
- Monitor Storage and Performance: Cloning large tables can consume storage and impact performance; plan accordingly.
Alternatives to Redshift CREATE TABLE LIKE
While LIKE is straightforward for schema duplication, sometimes other methods are preferable:
CREATE TABLE AS SELECT(CTAS): To copy schema and data in one step:
CREATE TABLE new_table AS SELECT * FROM existing_table WHERE 1=0;Using WHERE 1=0 ensures only the schema is copied, similar to LIKE.
- Manual Schema Definition: For complex schemas, define the table explicitly to have full control.
- Using SQL Client Tools: Many database tools can generate schema scripts for duplication.
Conclusion
The Redshift CREATE TABLE LIKE statement in Amazon Redshift is a valuable tool for efficient schema duplication. Its simplicity and speed make it ideal for creating backups, testing environments, or preparing schemas for data transformation. However, understanding its limitations and best practices ensures it is used effectively.
By leveraging Redshift CREATE TABLE LIKE, data engineers and analysts can streamline their workflows, maintain consistency across tables, and optimize their data warehousing strategies. Always consider your specific use case and combine it with other SQL techniques to achieve the best results.
References:
- Amazon Redshift Documentation: CREATE TABLE
- Amazon Redshift SQL Reference
- Best Practices for Redshift Table Design
If you need further assistance or practical examples, feel free to ask!