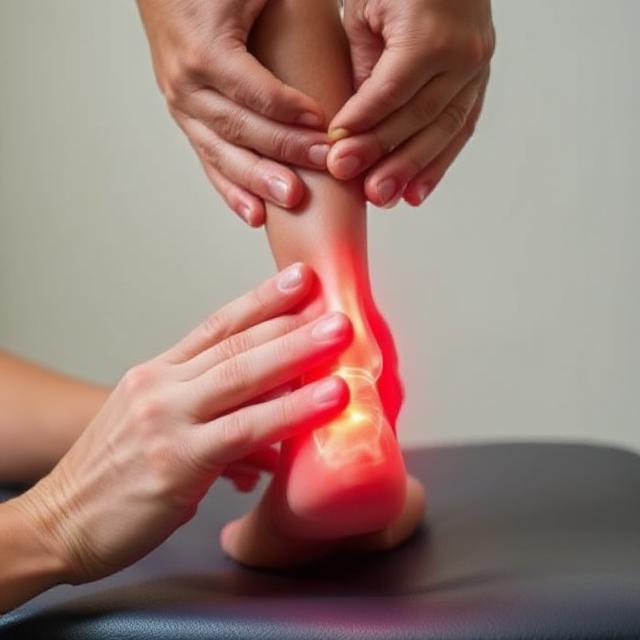
Introduction to Stress Fracture Heel Treatment
A stress fracture Heel Treatment in the heel, though relatively uncommon, can be a painful setback, especially for individuals who lead active lifestyles or spend long hours on their feet. Understanding the condition, its causes, and how it’s treated is essential for effective recovery and prevention. Below, we’ll explore what a stress fracture Heel Treatment in the heel entails, how it’s diagnosed, and, most importantly, the treatment options and preventative strategies available.
What is a Stress Fracture in the Heel?
A stress fracture Heel Treatment is a small crack or severe bruising within a bone that typically develops due to repetitive forces or overuse. When it occurs in the heel bone, also known as the calcaneus, it can sideline individuals from their usual activities for weeks or months.
Common Causes
Stress fractures in the heel often result from repetitive impact activities. Runners, athletes, and individuals in occupations requiring prolonged standing or walking are at higher risk. Common causes include:
- Overtraining or sudden increases in activity: For runners, ramping up mileage too quickly can overburden the heel bone.
- Poor footwear: Wearing unsupportive or worn-out shoes may fail to absorb adequate shock, increasing the stress on the heel.
- Foot structure issues: Conditions like flat feet or high arches can unevenly distribute pressure, predisposing the heel to stress injuries.
- Insufficient bone density: Osteoporosis or nutritional deficiencies can weaken bones, making them susceptible to fractures.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a stress fracture Heel Treatment in the heel can vary but often include:
- Localized pain in the heel that worsens with activity and improves with rest.
- Swelling or tenderness around the back of the foot.
- Difficulty bearing weight or walking.
- Persistent discomfort even at rest in advanced cases.
Recognizing these signs early is crucial for seeking appropriate treatment and preventing further damage.
Diagnosing a Heel Stress Fracture
Accurate diagnosis is vital to distinguish a stress fracture Heel Treatment from other conditions, such as plantar fasciitis or simple bruising. The diagnostic process generally includes:
Initial Assessment
A healthcare provider will start by discussing your symptoms, medical history, and activity levels. They’ll also perform a physical examination to locate pain points and rule out other potential issues.
Imaging Tests
- X-rays: While these are a common first step, stress fractures Heel Treatment may not be immediately visible on X-rays, especially in the early stages.
- MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging is more sensitive and can detect small fractures and surrounding soft tissue damage.
- Bone Scan: This test uses a small amount of radioactive material to highlight bone abnormalities and is useful when MRIs are unavailable.
Prompt and accurate diagnosis ensures the condition doesn’t worsen due to delayed treatment.
Treatment Options for Stress Fractures in the Heel
Treatment for heel stress fractures Heel Treatment often emphasizes rest, healing, and gradual rehabilitation. The severity of the fracture and individual circumstances will guide the course of action. Below are common treatment approaches:
Rest and Activity Modification
The fundamental step in treating a stress fracture Heel Treatment is to reduce or eliminate weight-bearing activities. This might mean:
- Using crutches or a walking boot to offload pressure from the heel.
- Avoiding high-impact activities like running or jumping until the bone heals.
Physical Therapy
Once the acute pain subsides, physical therapy can aid recovery. A physical therapist might focus on:
- Stretching and strengthening exercises for surrounding muscles to improve foot stability.
- Techniques to enhance flexibility and reduce stress on the heel during movement.
- Gradual reintroduction of weight-bearing activities.
Orthotics and Supportive Devices
Custom orthotics or cushioned shoe inserts can provide added arch support and reduce pressure on the heel. These devices are particularly beneficial for individuals with specific foot structure issues.
Medical Interventions
While conservative treatments suffice for most stress fractures Heel Treatment, more severe cases may require additional intervention:
- Surgery: Rarely, surgery may be necessary to stabilize the fracture using screws or plates, especially for non-healing fractures.
- Bone Stimulators: For delayed healing, electronic bone stimulators may encourage bone growth by applying low electrical currents.
Your healthcare provider will determine if advanced treatments are necessary based on the injury’s progress and response to initial therapies.
Tips for Recovery and Prevention
Recovery Guidelines
Healing from a heel stress fracture Heel Treatment requires patience and diligence. Here are some tips to optimize recovery:
- Follow medical advice: Whether it’s wearing a boot or attending therapy sessions, adhering to your physician’s recommendations is key.
- Gradual return to activity: Avoid rushing back into full activity too soon. Incremental increases in intensity can help prevent setbacks.
- Nutrition for healing: A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D supports bone health. Foods like milk, cheese, leafy greens, and fortified cereals are excellent choices.
Preventing Future Stress Fractures Heel Treatment
Preventative strategies can make all the difference in avoiding repeat injuries. Consider these tips:
- Strengthen your bones: Maintain healthy bone density through diet and, if needed, supplements. Weight-bearing exercises like walking or strength training can also help.
- Wear proper footwear: Choose shoes suited for your activity that offer ample cushioning and arch support. Replace them regularly to ensure effective shock absorption.
- Listen to your body: Pain is your body’s way of signaling a problem. Rest at the first sign of discomfort rather than pushing through.
- Cross-train: Mix low-impact activities, such as swimming or cycling, into your routine to minimize repeated stress on the heel.
Final Thoughts
A stress fracture Heel Treatment in the heel requires prompt attention and a committed approach to treatment and recovery. While rest and rehabilitation are critical, preventing future injuries is equally important. By recognizing risk factors, using proper footwear, and maintaining overall bone health, you can protect your heels and stay active without interruptions. Consultation with a medical professional is essential at every step to ensure personalized care and optimal healing progress.